What is glaucoma and what is the main cause?
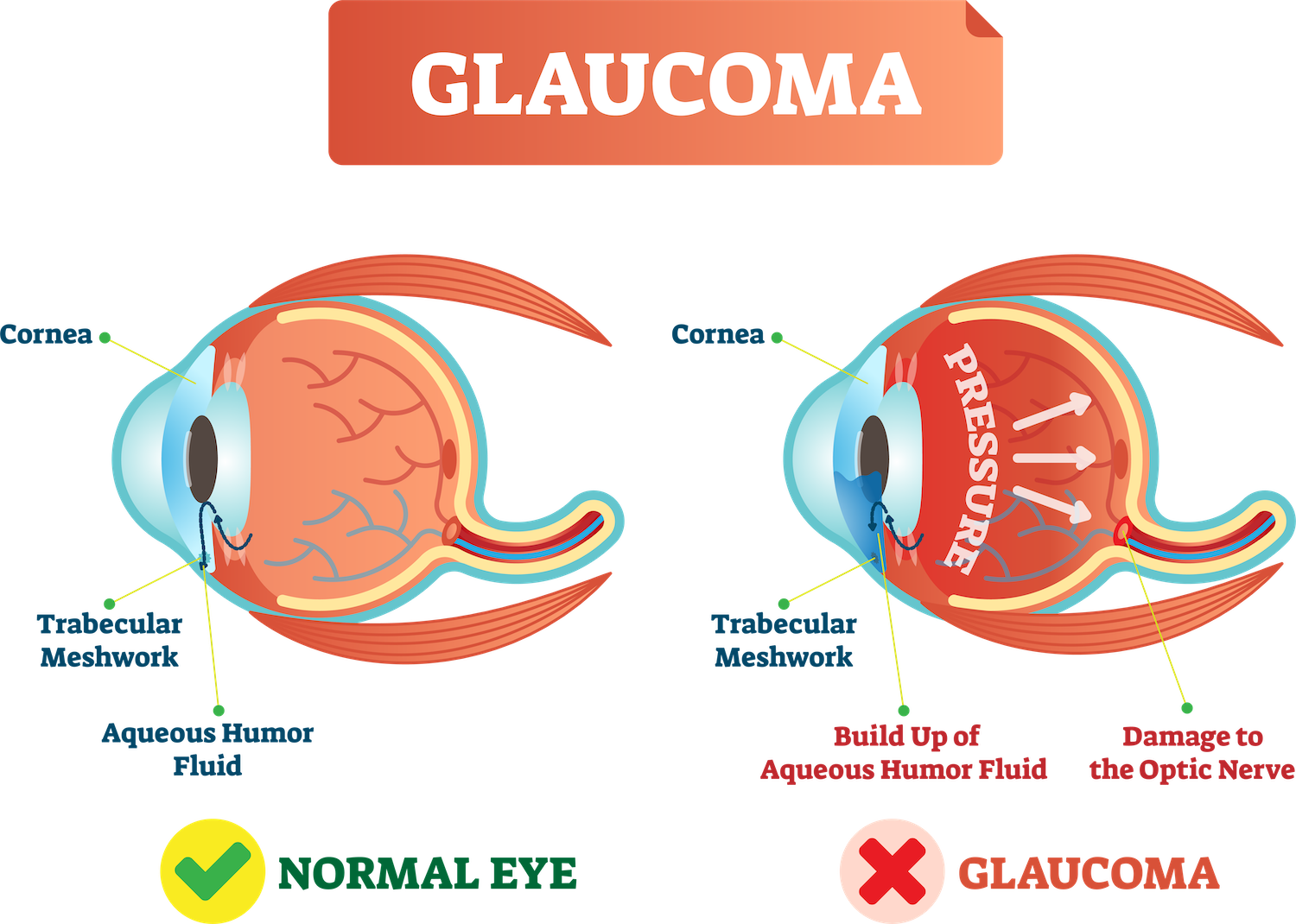
Glaucoma is a group of eye diseases that cause vision loss caused by damage to the optic nerve. If left untreated, glaucoma can lead to total blindness even in otherwise healthy eyes. One way to detect if this condition is developing is to pay attention for early signs such as peripheral vision loss or reduced night vision. Although causes vary from person-to-person, there are four common causes.
It's important to be aware of the different stages of glaucoma which range from no detectable damage in stage 1 all the way up to advanced uncontrollable pain with intense itching and ulceration during stage 5. In today's post we'll discuss what exactly glaucoma is, how it develops, and what its main cause can be for different individuals so you're better prepared moving forward!
What is Glaucoma? Definition and Overview
Glaucoma is a common eye disease that affects millions of people worldwide. It is a condition that damages the optic nerve, which is responsible for transmitting visual information from the eye to the brain. As a result, people with glaucoma may experience a loss of peripheral vision, tunnel vision, or even permanent blindness if left untreated.
Glaucoma can occur at any age, but it is more common in adults over the age of 60. It is essential for people to understand the symptoms of glaucoma and seek medical attention promptly if they notice any changes in their vision. Regular eye exams are also crucial in detecting and treating glaucoma before it leads to irreversible vision loss.
What is the Main Cause of Glaucoma ?
The main cause of glaucoma is an increase in pressure inside the eye, known as intraocular pressure (IOP). This increased pressure can occur when the eye’s drainage system becomes blocked, preventing fluid from leaving the eye. If left untreated, this increase in pressure damages delicate nerve fibers and causes vision loss. Other factors that may increase person’s risk of developing glaucoma include family history, older age, diabetes, eye trauma and certain medications.
The most common type of glaucoma is primary open-angle glaucoma, which occurs when the drainage system in the eye becomes clogged. This can be caused by an increase of pressure inside the eye, which occurs when fluid is unable to drain properly. With this type of glaucoma, vision loss usually starts in the peripheral or side vision. Other types of glaucoma include angle-closure glaucoma, normal-tension glaucoma and congenital glaucoma.
What are the First Signs Glaucoma is Developing?
Sometimes called the “silent thief of sight,” it often has no symptoms in its early stages and can go unnoticed for years. But that doesn’t mean there aren’t signs that glaucoma is developing. One of the first signs is usually a loss of peripheral vision. The ability to see objects to the side or above and below your central vision may become blurred or limited.
Another early sign can be changes in the optic nerve, which can be detected during a routine eye exam. If you have concerns about your eye health or are at risk for glaucoma, talk to your eye doctor about screening and prevention options.
Understanding the 5 Stages of Glaucoma
Glaucoma is usually classified into five stages, each of which it's own set of symptoms and treatments. It’s important to understand the different types of glaucoma in order to diagnose it earlier and start the right treatment plan.
Stage 1: Latent (Open Angle) Glaucoma. This is the earliest stage, and it usually doesn't cause any vision problems. It's usually detected during a regular eye exam by measuring the pressure in your eyes.
Stage 2: Mild Glaucoma. In this stage, you may start to experience some vision problems such as difficulty seeing at night or decreased peripheral vision. Your eye pressure may also be elevated.
Stage 3: Moderate Glaucoma. In this stage, the vision loss becomes more pronounced and you may start to experience blind spots in your vision. Your eye pressure may remain high or even increase further.
Stage 4: Severe Glaucoma. At this point, your vision is significantly affected and you may experience vision loss that cannot be reversed. Your eye pressure will likely remain high or increase, and if left untreated, can lead to complete blindness.
Stage 5: Advanced Glaucoma. This stage causes the most severe vision loss and is usually irreversible. At this point, your eye pressure has reached dangerously high levels and has caused significant damage to your optic nerve. If left untreated, you will experience total blindness.
Treatment for Glaucoma depends on the stage of the disease at diagnosis and what type of glaucoma you have. Treatments range from medication to surgery and can help slow down or stop vision loss. It is important to discuss your treatment options with your doctor to determine the best course of action for you.
Top 4 Risk Factors of Glaucoma
There are a few factors that can increase your risk of developing glaucoma. These include:
Age: Glaucoma is more common in people over the age of 40.
Family history: If someone in your family has had glaucoma, you may be more likely to develop it as well.
Ethnicity: Certain ethnicities, including African Americans, Latinos and Asians, are at increased risk of developing glaucoma.
Medical conditions: Diabetes, high blood pressure and heart disease can all increase your risk of getting glaucoma.
If you have any of these risk factors, it’s important to speak to your doctor about regular glaucoma screenings. That way, if you do develop the condition you can get treatments that may help protect your vision for years to come.
It’s important to have regular eye exams and talk to your doctor about any possible risk factors you may have. That way, if glaucoma does develop, you can take steps to protect your vision with a qualified medical professional.
Treatment Options for Glaucoma
If you are diagnosed with glaucoma, your doctor will recommend treatments based on the type and severity of condition. Generally speaking, treatments are designed to reduce pressure in the eye and slow or stop further vision loss. Depending on the type of glaucoma you have, treatment options may include:
Eye drops or topical medications to reduce the pressure inside your eye
Laser surgery, which can improve the drainage of fluid
Surgery to create a new drainage path for fluid
Oral medications to reduce pressure in the eye
It is important to follow your doctor’s instructions and take all necessary precautions when it comes to treating glaucoma. If left untreated, glaucoma can lead to irreversible vision loss and even blindness, so it is important to follow any recommendations your doctor gives you.
Additionally, lifestyle changes can also help reduce the risk of developing glaucoma or slow its progression. These include quitting smoking, exercising regularly, eating a healthy diet, and wearing sunglasses with UV protection.
Finally, it is important to understand that glaucoma cannot be cured and some vision loss may still occur even when treatments are successful. Therefore, it is important to take steps to protect your eyes from any further damage. This includes avoiding activities like contact sports or hazardous hobbies, and wearing protective eyewear when necessary.
TESTIMONIAL

Everything was explained. Everyone was helpful, cheerful, and competent. Dr. Paré was, as always, competent, helpful, and patient.

“My visit was awesome. The tech was fantastic and of course we love Dr. Hewitt.”

Dr. Park has my full faith and confidence for me to recommend her to whomever may read this. I am pleased she has joined the practice. Her professional and exceptional caring will be evident in seconds to her patients meeting her.
OFFICE HOURS
| Week Days | 8:00 - 4:00 |
| Saturday | Closed |
| Sunday | Closed |

